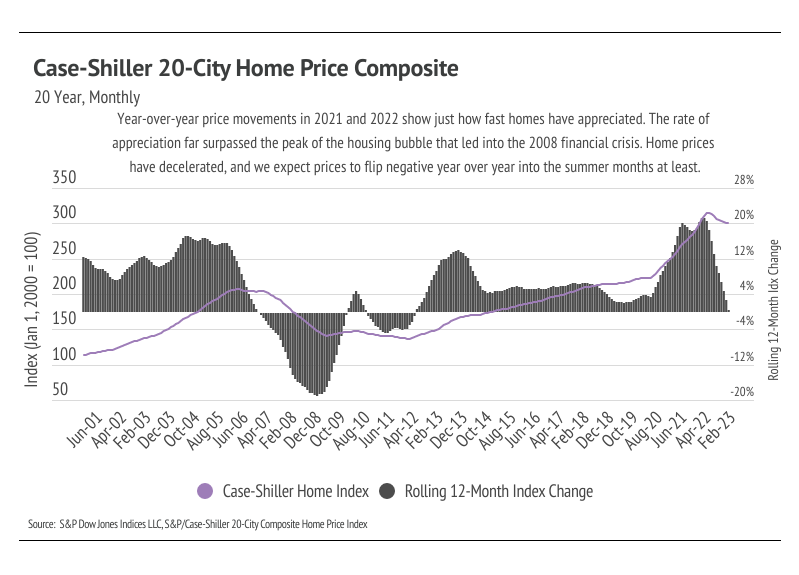
While we can say that we aren’t in a recession, it remains difficult to name the exact state of our economy. “Economic limbo” may be the right term, “uncertainty” certainly works, or “whiplash” fits. Three years post-pandemic, we are still trying to figure out the pre-pandemic economy, which grew with such stability from 2012 to 2020 that it was hard to imagine anything different. The pandemic hit and shifted our world from that of boundless, endless choice to a much smaller menu of options. Eat, work, buy, sleep, repeat. Asset prices soared. Consumers had money to spend and were eager to spend it. Easy credit conditions spurred price increases, especially home prices. The change in purchasing power in 2020 is hard to overstate. Due to falling interest rates, prices could rise 10% over the course of the year without changing the monthly cost of the mortgage. Said differently, a $500,000 loan taken in January 2020 cost the same every month as a $550,000 mortgage in December 2020. Interest rates remained consistently low in 2021.
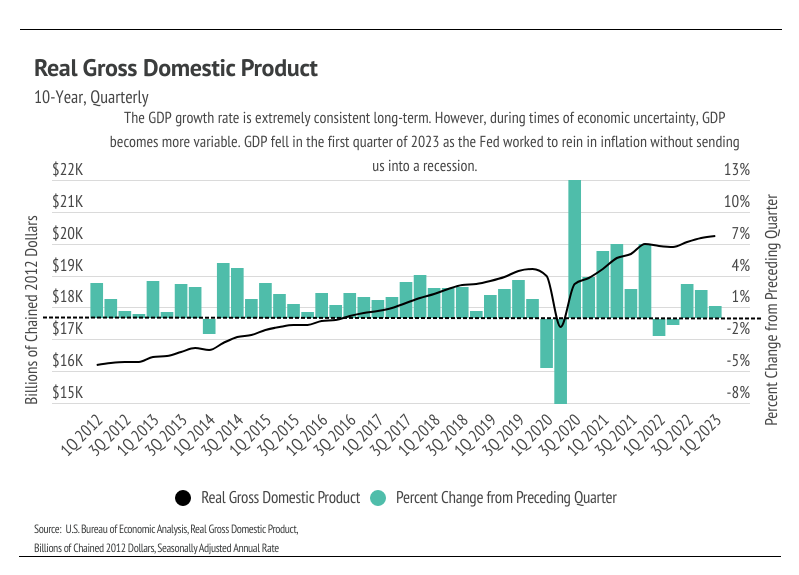
A record number of buyers were priced into the market, and about a million more homes were sold in 2021 than the long-term average. However, skyrocketing inflation in 2021, in hindsight, was an obvious sign that the easy monetary policy was coming to a close, thereby creating the opposite effect of what happened in 2020 and 2021. The key takeaway is consumers felt wealthy and, to a large extent, were wealthier. Fewer options and opportunities to spend money led to more savings and wealth. How we feel means a lot when making big financial decisions. For many, if not most people, those feelings have changed, even if everything is technically fine on an individual level. Not that everyone (or anyone) ties their overall sense of well-being to Gross Domestic Product, an indicator of the economic health of a country or state, but recently released Q1 2023 data indicate that GDP fell from the preceding quarter, which isn’t surprising given the Fed’s effort to slow the economy. However, declining growth isn’t usually associated with rising consumer sentiments.
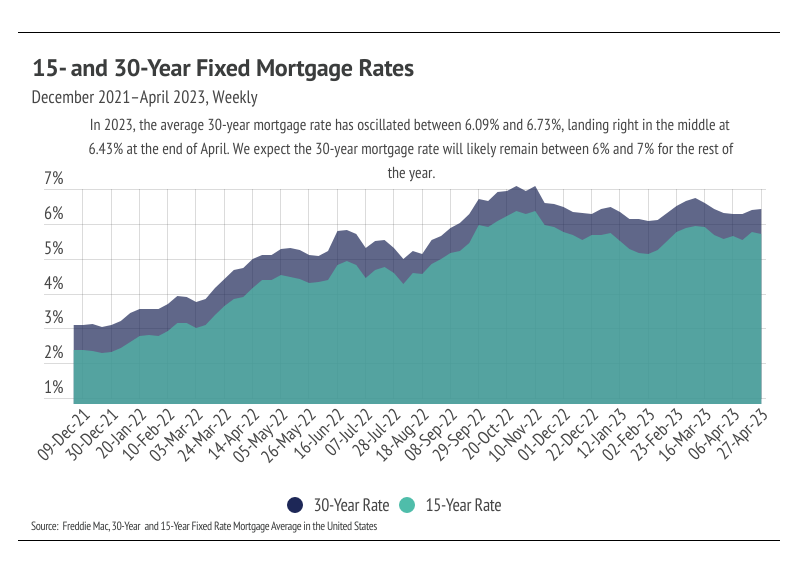
The Fed, which coincidentally met right after the March Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank failures, and then again right after the First Republic Bank failure in May, chose to raise their benchmark rate by 0.25% in both instances in a continuing effort to combat inflation. Banks are tightening their credit standards after the bank failures, so the Fed had less of a need to raise rates after increasing its benchmark rate 5% in the past 14 months. As the Fed assesses the impact of continued rate hikes and the fragility of the banking system, Fed Chair Jerome Powell indicated a real possibility they wouldn’t continue hiking rates this year, although there will certainly be no rate cuts. In terms of mortgage rates, we expect them to hover around 6-7% for the rest of the year.
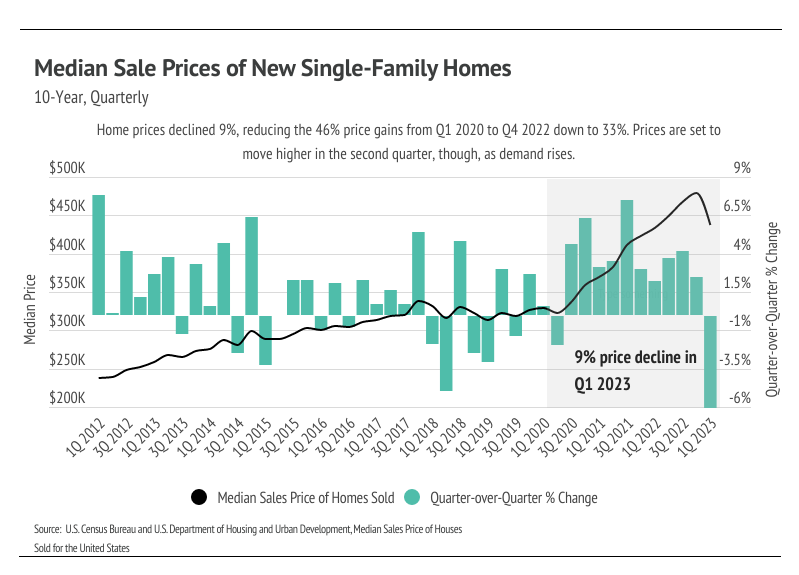
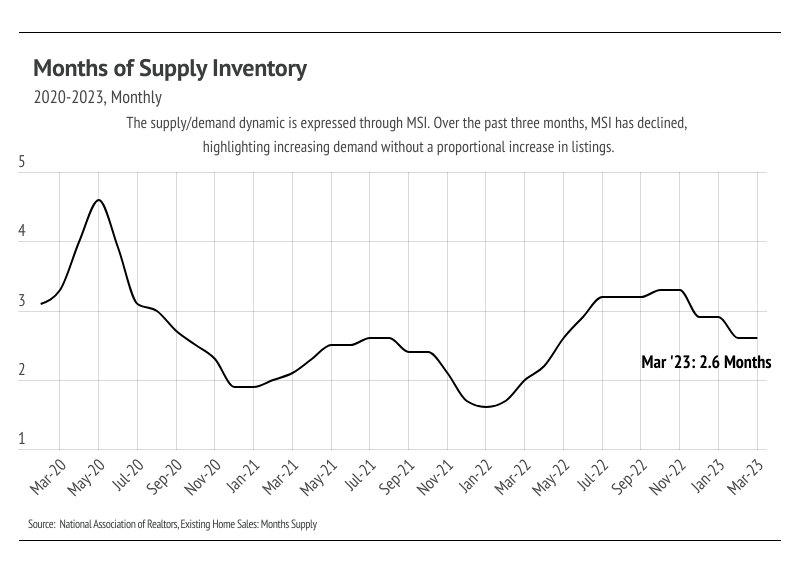
High rates coupled with high inflation negatively impacted consumer sentiment. Just as buyers were priced into the market in 2020 and 2021, they were priced out of the market in 2022. If we ignore everything except for rate increases, we would expect fewer buyers in the market. Additionally, if we have an outsized number of transactions, as we did in 2021, we would expect fewer buyers and sellers the following years because the same people don’t generally buy and sell residential property every year. Rates were so low that it was both a good time to buy and a good time to sell. Now, the housing market has to deal with both high rates and fewer market participants. Inventory is low, largely due to far fewer new listings than average coming to market. Supply of homes is low enough that, even though demand is lower on an absolute basis, it’s high relative to the number of available homes.
Different regions and individual houses vary from the broad national trends, so we’ve included a Local Lowdown below to provide you with in-depth coverage of your area. In general, higher-priced regions (West and Northeast) have been hit harder by mortgage rate hikes than less expensive markets (South and Midwest) due to the absolute dollar cost of the rate hikes. As always, we will continue to monitor the housing and economic markets to best guide you in buying or selling your home.
Big Story Data

# # #
It’s been Jennifer Burden's mission to help others succeed in the San Francisco market since 2004. She considers owning real estate to be a worthwhile financial and personal endeavor, and because she’s witnessed the life-changing power of real estate since she was a child, she works with unwavering dedication to create positive experiences for her clients.





